(Continued from the previous article)
 At present, PDPSI is built on 11 standards. We shall analyze what are the 11 standards that comprise of the PDPSI and the implementation specifications associated with it and how they relate to the “Certification” process.
At present, PDPSI is built on 11 standards. We shall analyze what are the 11 standards that comprise of the PDPSI and the implementation specifications associated with it and how they relate to the “Certification” process.
PDPSI has adopted the HIPAA model of “Standards” and “Implementation Specifications”.
By including implementation specifications in a statutory law, HIPAA made 7 standards without implementation specifications and 23 Required implementation specifications as part of the legal prescription. At the same time it left 22 implementation specifications as “Addressable” meaning that the management of a covered entity can take a view on whether thee 22 implementation specifications need to be implemented and if so whether they can be implemented in a manner different from what is suggested in the law.
In other words, HIPAA prescribes 30 statutory prescriptions on how to safeguard the protected health information by the covered entities and 22 other guidance indications that are optional with the condition that if they are replaced with alternatives, sufficient justification has to be provided through documentation.
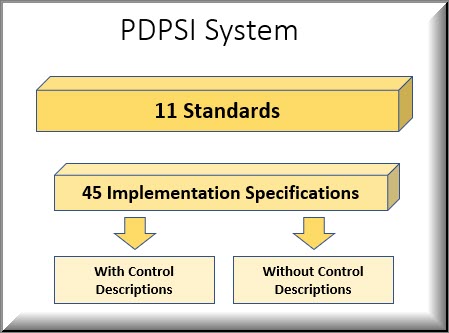
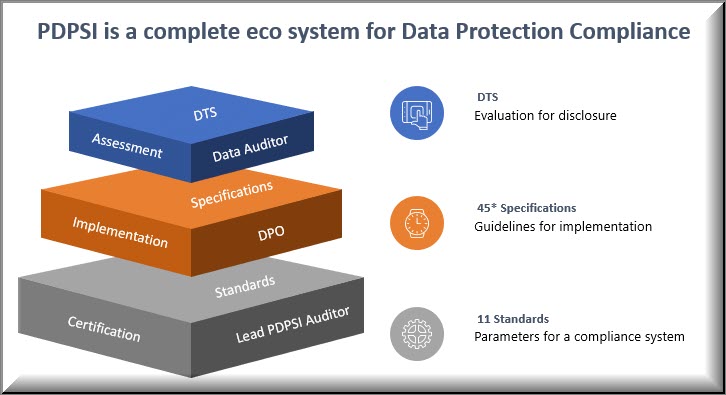
PDPSI is currently designed on 11 standards and 45 implementation specifications. But under PDPSI, the standards and implementation specifications are used differently from HIPAA. The PDPSI standards are defined for the conduct of PDPSI audit by a lead PDPSI auditor.
However the implementing company is provided with 45 guidance indications which can be used by the Data Fiduciaries and Data Processors. The documentation of whether these 45 implementation specifications are used in toto or some of them replaced with other controls and if so the reasons thereof, is addressed through one of the documents namely the “Implementation Charter” which is one of the 11 standards recommended. The PDPSI auditor will evaluate the implementation of the 11 standards reflected in the 45 implementation specifications along with the logic presented in the Implementation charter on why one or more of the suggested specifications are ignored or replaced.
The PDPSI auditor’s responsibility is in verifying the implementation of the standards and the implementation specifications adopted in the Implementation Charter and provides his certificate on whether the implementation system is set to work reasonably. The implementation specification includes what may be called “Controls” in other systems .
While the Standards and the Implementation specifications are created by the PDPSI agency (except to the extent the implementation specifications are modified through the implementation charter), the controls are created by the organization themselves.
A few of the key implementation specifications are explained in the PDPSI specification itself to the next level where they become “Control Descriptions”. But most of the other specifications are left without the subordinate “Control Level Description” because it is felt that the industry already has many best practice alternatives for these specifications. The “Control Descriptions” which are provided as part of the PDPSI documentation are those which may not be commonly used by the industry.
To this extent the “Implementation specification with control description” is similar to the “15 Standards with implementation specifications” in HIPAA and the “Implementation specification without Control Specification” is similar to the 7 standards without implementation specifications in HIPAA”.
The structure of PDPSI will therefore look like the following.
Naavi
…. To Be continued