We have been discussing the different aspects of the Personal Data Protection Standard of India. (PDPSI). During these several articles, we have discussed the philosophy behind the PDPSI and some of the controls which require a special mention.
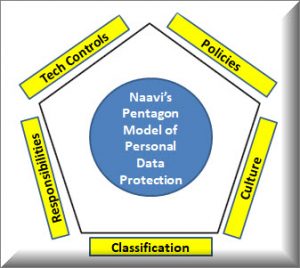
In continuation of our exploration of PDPSI, I would like to present the “Pentagon Model of Personal Data Protection” which provides a quick overview of the PDPSI approach.
The model is presented in the picture above. Naavi has earlier adopted the Pyramid Model for Information Security Implementation and a Pentagon model for Information Security Motivation
The pyramid model was appropriate for prioritization but the closed polygon model was found more suitable to represent the Information Security Motivation. A similar model appears appropriate for representing the requirements of the Personal Data Protection also.
The difference between the hierarchial model of the pyramid and the closed model of the polygon is that the hierarchial model is meant to be built level by level while the polygon model would require all wings to be in place simultaneously to close the polygon.
Since “Pentagon” represents security in general, we have adopted the pentagon model and put all requirements identified under PDPSI into the five categories which form the five boundaries of the Personal Data Protection pentagon.
To understand the five elements of the pentagon, let us analyze each of them with reference to our earlier detailed articles.
Element 1: Classification
As we have discussed in detail, (Article 1:Article 2) “Data Classification” is the starting point for the exercise and the foundation of a proper construction of Privacy by design. Data Classification also defines the scope of the compliance exercise since it maps the Data Protection law to which the compliance needs to be bench marked.
Element 2: Responsibilities
The responsibilities under PDPSI does not start and end with the DPO. DPO will remain the pivot around whom the responsibility is shared across the organization starting from the Board and the Data Protection Committee at the top to “Internal Data Controllers” spread across the organizations handling different functional responsibilities. This system of diversified responsibility recognizes the practical problems that a DPO would face in an organization particularly if it is spread across different functions and different geographical locations. Once the functional management of data and its security are in proximity, the implementation of any policy becomes easier.
Element 3: Tech Controls
Technical controls of Information Security are well researched and there is a lot of knowledge and skill in organizations around the world. These controls in the form of different hardware and software devices/applications provide solutions for meeting the CIA aspects of Information security and the extended concepts of accountability which includes Authentication and Non Repudiation. The Firewalls, IDS, Anti Virus, Access Control, Encryption, Digital Signature, version control, Data Leak Prevention systems, Multi factor authentication systems, the DRP/BCP systems, Forensic devices, etc all form the control tools under this head.
Element 4: Policies
The Policies part of the pentagon represent all the different policy and procedure documents that are required under the data protection laws including the Information Security policy, Privacy Policy, the Notification, Business Associate policy, Whistle Blower Policy , legitimate interest policy, Incident management policy, Data Disclosure cum Breach Notification policy, Business Agreement Control policy, HR recruitment, termination, sanction policies, the BYOD, Hardware/Software purchase policies, the web and email usage policies, documentation policies etc are all part of this segment of compliance.
Element 5: Culture
Apart from the Technical and Legal aspects of compliance addressed by the two earlier elements, the “people” aspect and in particular the “Behavioural Aspects of People” that affects the compliance is an important issue in itself. This may include the awareness building, motivation of people to be compliant, along with the incentives and disincentives to ensure that a proper “Data Protection Culture” is built in the organization.
While Classification and Responsibility assignment are essentially a one time exercise (except for changes that need to be accommodated from time to time), the three other segments require continuous monitoring and may also require different skills and knowledge. In large organizations three different experts may be required to address these three issues differently or the DPO should have the multi dimensional expertise.
This model breaks down the PDPSI into 5 elements for easy management. I suppose that this Pentagon model of Personal data protection would provide some clarity to organizing the Data Protection Compliance exercise in an organization.
Naavi