To Be compliant with Data protection or Privacy Protection through Personal Data Protection, an organization needs to implement a systematic approach like a project implementation. The “Privacy By Design” is a term used in the industry to indicate the approach.
In implementing an effective Personal Data Protection Program (PDPP), we need to consider that the most important part is to
a) Involve the entire work force in the compliance plan as a Team Effort
b) Keep the workforce motivated to implement the plan and maintain it as a continuing requirement.
Naavi recommends a Six step process to motivate the workforce to collectively implement the Privacy Program for an organization.
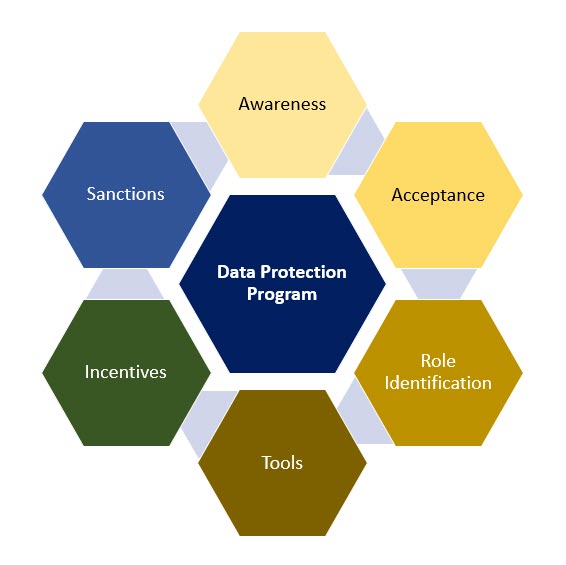
The six steps shown in the diagram as six elements of a Hexagon are
-
- Awareness
- Acceptance
- Role Identification
- Tools
- Incentives
- Sanctions
Awareness building is the common implementation step which is easily understood as conducting necessary trainings so that target audience (Employees) understand the requirements of the Data Protection Laws. This can be done at two levels, namely one at the Management Level and another at the workforce level.
Acceptance Building is a process where the workforce agree from the bottom of their heart the learnings of the awareness building exercise. A commitment from the member of the workforce to be compliant is always a good strategy to ensure that trainings donot remain only matters for ticking the check boxes.
Role Identification is a process where from the knowledge of what is required for data protection compliance built over the awareness building, is applied to an individual’s work responsibilities so that they can identify whether they do access personal data and if so how within their sphere of influence they need to implement the compliance requirements.
Tools provision is the responsibility of the organization and consists of Policy documents (properly explained to the workforce) and technical tools required for discovery of personal data, consent tagging, Encryption, data leak prevention etc.
Incentives are an important aspect of positive motivation so that good compliance culture exhibited by the workforce is rewarded in some manner whether financially or otherwise.
Sanctions are also essential since non conformance need to have a consequence without which the value of Incentivisation also will be less and complacency will set in.
This Hexagonal Approach to Data Protection Motivation is inspired by the Theory of Information Security Motivation and the Pentagon model that Naavi had published several years back.
As had been indicated in the Pentagon model, where five elements of motivations were considered as five walls of a pentagon rather than a hierarchical model of one after another, the Hexagonal Model of Data Protection Compliance should also be considered as a “Compact Hexagon” where each of the elements are walls of the Hexagon and are closed.
 As a Closed Hexagon, all six elements are expected to be present simultaneously and not built on a hierarchical model where some elements like Training are provided with Policy documents and expect the workforce to maintain a compliance culture.
As a Closed Hexagon, all six elements are expected to be present simultaneously and not built on a hierarchical model where some elements like Training are provided with Policy documents and expect the workforce to maintain a compliance culture.
FDPPI’s framework of Data Protection Compliance Standard of India (DPCSI) is geared towards implementing a compliance program in conformity with this Hexagonal motivational model.
The “Distributed Responsibility” concept used in DPCSI is a unique binding factor that enhances the efficiency of the Compliance program and to make it work, this Hexagonal Model of motivation would be useful.
Comments welcome.
Naavi